How To Find Place Value And Face Value
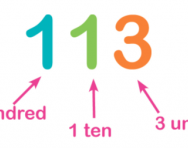
A adept understanding of place value (the value of each digit in a number) is vital in primary-school maths. Our parents' guide explains how your kid will exist taught about units, tens, hundreds and thousands with number lines, arrow cards and more, too as outlining how place value is used to help children visualise calculations.
What is place value?
Place value is the value of each digit in a number. It means understanding that 582 is made up of 500, fourscore and 2, rather than 5, 8 and 2.

How are children taught to understand place value in KS1?
In school two maths aids are used to help make place value clear to children.
Dienes blocks are blocks in which cubes represent units / ones, rods of ten cubes stand for tens, flats of 100 cubes correspond hundreds and blocks of 1000 cubes represent thousands:
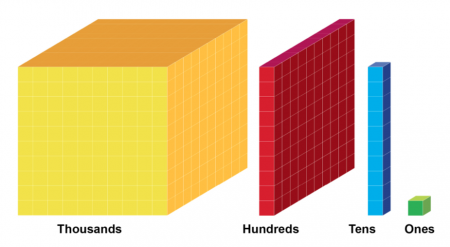
In Primal Stage 1, a child might be given some 10 and units (ones) Dienes blocks and asked to make a number such as 43. They would need to select iv tens rods and 3 ones blocks. This makes it very clear to them that a 2-digit number it made up of tens and ones. It also helps them to practise counting in tens.
Arrow cardswait like this:
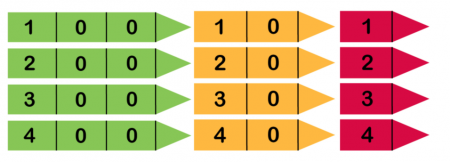

A kid might be asked to make the number 34 using arrow cards. They would demand to take the 30 and the 4 and put them together so that the arrows were lined up. This again helps to make articulate that a ii-digit number is made up of tens and ones.
Information technology is absolutely vital that children understand place value before they can go onto adding and subtracting two-digit numbers.
Place value in KS2
In Year 3, children might be given Deines blocks and arrow cards to help them with adding a pair of two-digit numbers. This would enable them to division the numbers, then that they could add the tens first and then the units. A Year 3 child would besides be expected to know the place value of digits in 3-digit numbers.
In Year 3, children also need to know what happens to a number when it is multiplied past 10 or 100. Information technology is really important hither that they are enlightened that the number moves to the left, rather than talking about 'adding zeros' (when children move onto dividing by 10 to find a decimal answer, they will not be able to employ the strategy of adding or removing zeros).
This is a mutual method used by teachers to testify children how to multiply by ten:
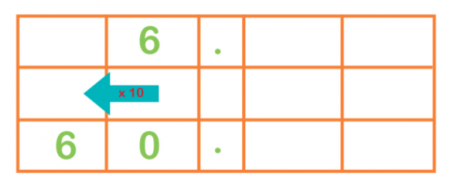
When multiplying half dozen by ten, the number moves to the left and a zero is put in, so the number becomes 60.
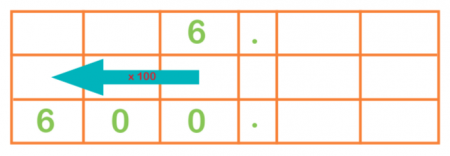
If yous multiply 6 past 100, the number moves two places to the left and zeros are put in, then the number would become 600.
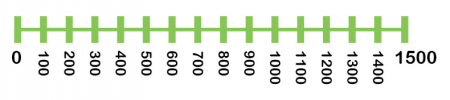
In Yr 4, children would need to employ their knowledge of identify value to piece of work out sums and difference of pairs of multiples of 10, 100 or m. They might be asked to mentally work out 80 + 40 in which instance they would demand to 'cross 100' to observe the answer 120. They might be asked to work out 700 + 600 or 8000 + 3000, in which case they would be crossing g and 10,000. A number line can be helpful in these instances.
Year four children too need to start to empathize the place value of decimals. A blank hundred square is a proficient way of demonstrating this:
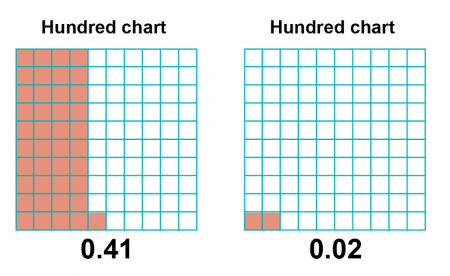
With the to a higher place two decimals, you tin get in clear that 0.41 is 41/100 and 0.02 is two/100.
Sometimes teachers use modest whiteboards marked like this:
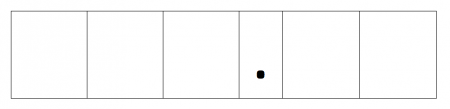
onto which children have to write a number that the instructor has said out loud. For example: the child might exist asked to write the number 5.72. They might and so be asked to add 0.i to this number, at which indicate they would demand to change the number to 5.82. They might be asked to subtract 0.01, at which point they would need to change the number to 5.81.
In Year 4 children need to learn how to split up numbers by 10 and 100. Teachers unremarkably teach this using this method:
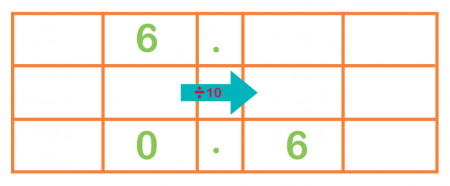
When dividing six by x, the number moves 1 place to the correct and becomes 0.6.
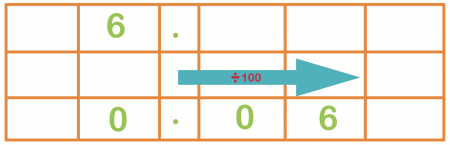
If you lot split up 6 by 100, the number moves two places to the right and becomes 0.06.
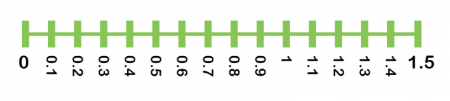
In Year 5, children demand to use their knowledge of place value to piece of work out sums and differences of decimals. For example, they would need to know that calculation 0.8 and 0.four results in 'crossing 1' because the respond is 1.2. A number line can be helpful in demonstrating this:
In Year vi, children need to know their knowledge of identify value to piece of work out multiplication and division of decimals. For case, when working out 0.six x iv, they would demand to know that this is the same equally working out half-dozen x 4 = 24, but then the reply needs to exist divided by 10 (because 6 divided by ten is 0.6) to brand the reply 2.4.
Source: https://www.theschoolrun.com/what-place-value
Posted by: halcombruimilot.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Place Value And Face Value"
Post a Comment